The author's research group is mainly engaged in the molecular mechanism of microRNA and circRNA in the development of heart disease. Recently, its laboratory used Arraystar circRNA chips to screen myocardial tissue samples of different ages and found that circ-Amotl1, which is highly expressed in neonatal cardiomyopathy, plays a role in myocardial repair by interacting with proteins PDK1 and Akt. positive effects. The article was published in the international journal Theranostics (impact factor 8.712 ). (Chip experiments are provided by Kang Cheng Biotech)

Research Background:
According to WHO statistics, ischemic heart disease is one of the leading causes of death. Although the myocardium has a certain ability to regenerate after infarction, this limited remodeling is usually insufficient. Myocardial injury induces senescence and death of cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. Dead cells gradually replace fibrous scars, disrupting normal ventricular structure and function. Crucially, myocardial ageing or aging reduces its ability to remodel and regenerate, further exacerbating the risk of cardiovascular disease and injury. Understanding the molecular basis of cardiac remodeling and heart aging is critical to the treatment and development of this serious disease.
Akt plays an important role in many cellular processes such as cell proliferation, survival and apoptosis. Under normal conditions, Akt is inactive in the cytoplasm. Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase (PDK) phosphorylates Akt, making it a pAkt, which plays a regulatory role in the nucleus. Professor Yang recently discovered that a new class of non-coding RNAs (circRNAs) may play a crucial role in the cell cycle progression of cardiac remodeling. Professor Yang has found that some circRNAs have been shown to play a role in miRNA sponge, but most of the mechanisms of action are still unclear. Previous studies have found that circ-foxo3 is highly expressed in the aging phenotype of injured myocardium and can cause aging. Professor Yang speculated that circRNAs may play an important role in regulating myocardial tissue regeneration.
Research ideas:
In order to study the role of CircRNA in myocardial repair, the authors selected three neonatal cardiomyopathy and three elderly cardiomyopathy mixed tissue samples using the US Arraystar circRNA chip for high-throughput screening. Molecules with more than twice the difference were screened from the samples, and the circ-Amotl1 molecule reported by the host gene in cardiomyopathy was selected as an indicator for subsequent studies. Circ-Amotl1 is highly expressed in neonatal myocardial samples, which are derived from the third exon of the Amotl1 gene (Angiomotin-like 1) and are circRNA molecules formed by a single exon. qPCR verification showed that the expression of circ-Amotl1 showed a gradual decline with age.
In functional studies, the authors constructed a circ-Amotl1 overexpression vector, which was verified in multiple cell lines such as MCF7 and YPEN, and found to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis. RNAi against circ-Amotl1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis. In a mouse model of tetracycline (DOX)-induced cardiomyopathy, injection of the circ-amotl1 plasmid into mice significantly ameliorated myocardial symptoms.
In terms of molecular mechanism, the paper focused on the overexpression of circ-Amotl1, which caused an increase in pAkt, and inhibition of Akt inhibited the effect of circ-Amotl1 on cell proliferation. Further, the authors extracted the circ-Amotl1 complex by RIP experiment, which proved that it does not function through miRNA sponge, but by binding Akt and PDK1, activates Akt pathway and promotes its nuclear regulation.
Research route:

The results show:
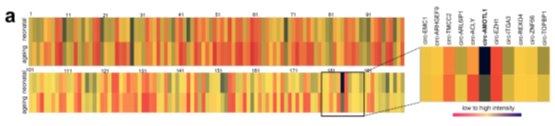
Figure 1: Differential circRNA clustering map for Arraystar CricRNA chip screening
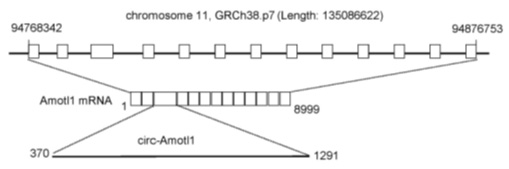
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of the positional relationship between circ-Amotil and the host gene Amotl1 in the genome
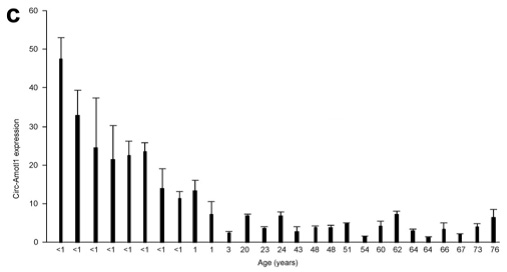
Figure 3: qPCR verified that circ-Amotil is highly expressed in neonates and decreases with age
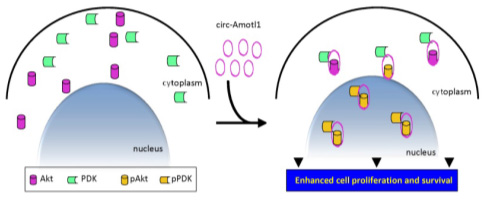
Figure 4: Circ-Amotil1 promotes Akt phosphorylation and transport into the nucleus by binding to Akt and Pdk1, thereby promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation
Significance:
In this paper, Arraystar circRNA microarray was used to screen myocardial tissue of patients of different ages, and the role of circRNA in myocardial repair was explored. Studies have shown that circ-Amotl1 is a highly expressed molecule in the neonatal heart and can enhance myocardial function. By binding Akt and PDK1, circ-Amotl1 induces Akt phosphorylation and pAkt nuclear transport, activates Akt signaling pathway, promotes cell survival and proliferation, and protects against DOXs-induced cardiomyopathy. circ-Amotl1 can be used as a potential therapeutic agent for myocardial repair.
Original source:
A Circular RNA Binds To and Activates AKT Phosphorylation and Nuclear Localization Reducing Apoptosis and Enhancing Cardiac Repair. Theranostics.2017; 7(16):3842-3855
Fast Shipping Laser Distance Sensor
Hi there,
We create a new payment method online for you, so that all of our customers, and you can get the samples quickly. With the competitive prices online, it is easy to operate and finish your sample orders of JRT Laser Distance Sensor. It's really amazing, right? Let's go!
Greetings

Fast Shipping Laser Distance Sensor,Serial Laser Distance Sensors,USB Laser Distance Sensors,RS232 Laser Distance Sensors
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.irdistancesensor.com