Scientists at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis are using micro-wireless LEDs to identify and map neural circuits in the brain in order to use LED light-activated genes to control individual brain cells. They acquire photoactivated genes from specific types of neurons and insert them into the mouse brain. The sparkling light then enters the mouse's brain, which activates the neurons or inhibits their activity. The study may one day provide better treatment for depression, addiction and anxiety.
This innovative research work has been recognized and funded by the EUREKA grant program. The EUREKA grant was established by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to fund innovative research projects, establish new methods and concepts to solve major problems or open up new areas of research. The National Institutes of Health provides 12 to 18 such grants each year.
With this grant, Dr. Michael R. Bruchas, an assistant professor of anesthesiology, and his colleagues will use micro-LED devices for research. In a recent study, Bruchas and his colleagues put this LED device, which is thinner than the hair, into a specific part of the mouse brain, a position called the "brain reward." When a mouse pokes its nose in a way that is confusing, the light-activated neurons release a happy-related chemical, dopamine.
A four-year, $1.2 million grant made it possible for Bruchas and his team to develop specialized light-sensitive G-protein coupled receptors so that researchers can use light to control cellular signals in the brain. These new receptor tools will be implanted in the mouse brain along with wireless micro LED devices to reveal more molecular and cellular activities under stress, addiction or depression.
Unlike most previous optogenetic experiments, the miniature LEDs used by researchers at the University of Washington are wirelessly controlled and easy to operate. Animals participating in the experiment are free to move without being controlled by limited wires.
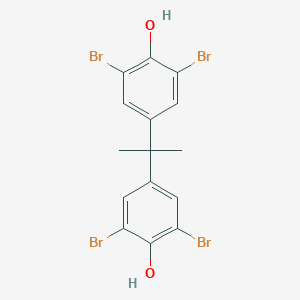
Tetrabromobisphenol A CAS No.79-94-7
Tetrabromobisphenol A Basic Information
Product Name: Tetrabromobisphenol A
CAS: 79-94-7
MF: C15H12Br4O2
MW: 543.87
EINECS: 201-236-9
Mol File: 79-94-7.mol
Tetrabromobisphenol A Structure
Melting point 178-181 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 316 °C
density 2.1
storage temp. 2-8°C
solubility Insoluble
form neat
Tetrabromobisphenol A,Tetrabromobisphenol A Msds,Tetrabromobisphenol A (Tbbpa),Tetrabromobisphenol A Bis (2 3-Dibromopropyl Ether),Tetrabromobisphenol A Bis
ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com