Relaxation process
In the NMR phenomenon, relaxation refers to the phenomenon that when the nucleus resonates and is in a high-energy state, when the RF pulse stops, it will quickly return to the original low-energy state. The process of recovery is called the relaxation process, which is an energy conversion process that takes some time to reflect the interaction between protons in the mass subsystem and the environment around the proton.
The completion of the relaxation process is carried out in two steps, that is, the longitudinal magnetization vector M z is restored to the initial equilibrium state M 0 and the transverse magnetization M xy is attenuated to zero. These two steps are started simultaneously but independently, as will be briefly described below. Longitudinal relaxation process and relaxation time T 1 .
A common principle of thermodynamics is that all systems tend to their lowest energy state. The longitudinal relaxation process is the heat exchange between protons and surrounding materials, or protons diffuse excess energy through the crystal lattice, causing it to transition from high energy level to low energy level. Therefore, this process is also called spin-lattice relaxation process. .
The T1 relaxation time describes the spin system, the speed of the two-level layout from the beginning to the thermal equilibrium.
The figure below shows the relaxation process of a system consisting of four protons.
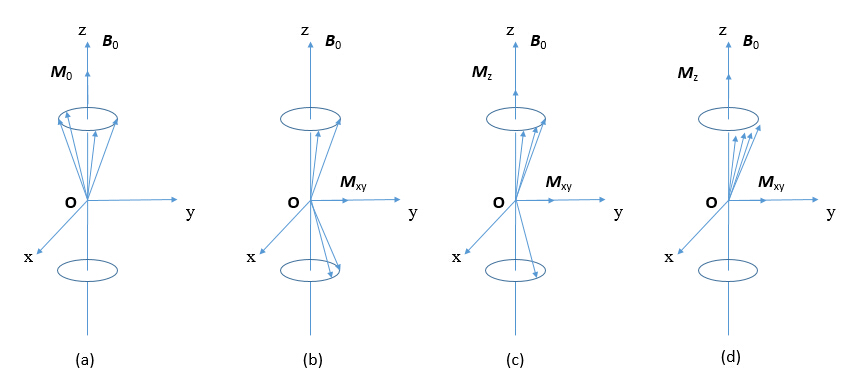 (a) indicates the initial equilibrium state, four protons are at the low energy level to form the initial longitudinal magnetization vector M 0 ; (b) is the non-equilibrium state after the π/2 pulse excitation, and the low-energy high-energy protons are equal. At this time, the longitudinal magnetization is zero;
(a) indicates the initial equilibrium state, four protons are at the low energy level to form the initial longitudinal magnetization vector M 0 ; (b) is the non-equilibrium state after the π/2 pulse excitation, and the low-energy high-energy protons are equal. At this time, the longitudinal magnetization is zero; (c) and (d) represent the longitudinal relaxation process in which the longitudinal magnetization gradually recovers from zero to the initial condition, and the transverse relaxation process is not considered here.
Chengdu proportional to the longitudinal magnetization M z M 0 component to restore the equilibrium state speed and they leave the rest position, when the π / 2 pulse, the obtained expressions recovery of the longitudinal magnetization M z:
In the above formula is called longitudinal relaxation time T1 (longitudinal relaxation time) T1 for short, typically with M z recovery time from zero to 63% M 0 required to determine T1, i.e. longitudinal relaxation time T1 of M z The time required to recover to 0.63 M 0 , as shown below:
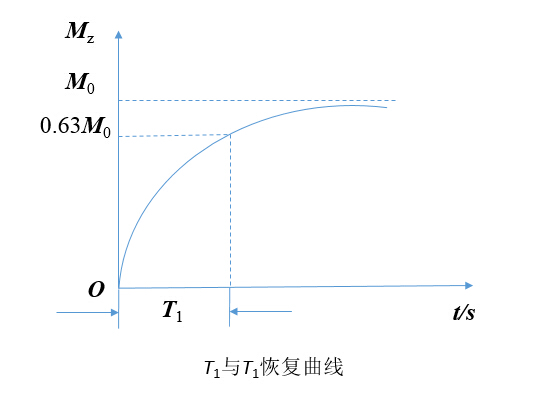
The magnitude of the longitudinal relaxation time T1 depends on the interaction between the external magnetic field and the protons and the surrounding environment (ie, the nature of the tissue). It is an intrinsic property of the organization. After the external magnetic field is given, the T1 values ​​of different tissues have corresponding fixed values, but the T1 values ​​of different tissues are very different.
The external magnetic field B 0 (the magnitude of B 0 ) also has an effect on the longitudinal relaxation time T1 of the tissue, and the longitudinal relaxation time T1 of most tissues becomes smaller as the B 0 of the external magnetic field decreases. However, this is not the case for pure water (also known as free water or free water), and its T1 value does not change with the strength of the external magnetic field.
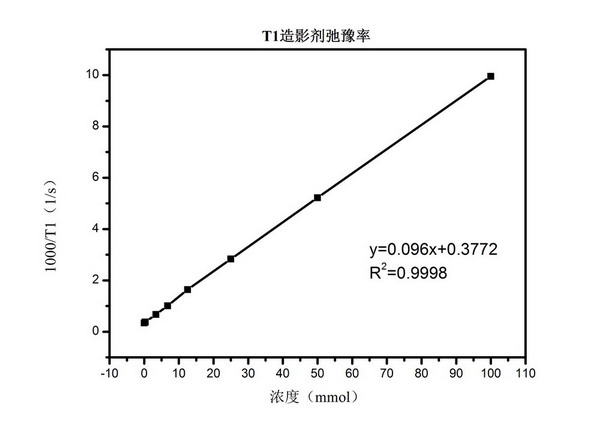
Application of longitudinal relaxation time - test of contrast rate of contrast agent:The NMR contrast agent is a preparation used to enhance the contrast effect of the image, which indirectly changes the intensity of the tissue signal by affecting the relaxation speed of the surrounding tissue, and increases the contrast of the tissue or the organ. According to the imaging features, the contrast agent can be divided into a positive contrast agent and a negative contrast agent. A positive contrast agent will make the image brighter and whiter than normal, mainly affecting the change of the longitudinal relaxation time T1 value, and the positive contrast agent is also called T1 contrast agent. The relaxation efficiency of the contrast agent is one of the main parameters for evaluating the performance of the contrast agent .
The figure below shows the T1 contrast agent relaxation rate test curve:
 Contact: Chen Gong | Contact Phone | E-mail:
Contact: Chen Gong | Contact Phone | E-mail: 
Casing Tester is a viral transport medium tube with Swab, which is a long cotton swab with a medical tube, dipped in a small amount of saliva or other secretions of the person to be tested, and then tested for the virus. It is best not to use drugs before the test, so as not to affect the test results. The method is simple, convenient and fast to operate, can produce results quickly, and guide clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Casing Tester,Throat Swab,Disposable Sampler Swab,Disposable Flocked Swab, Oral Saliva Swab Viral Transport Medium Tube with Swab
Jiangsu HXRT MD Co.,Ltd , https://www.jshxrtmed.com