
In December 2017, Dr. Adrien Moya of the Seventh Congress of Paris published an article on Stem Cell to study the glucose metabolism of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to analyze the extremely low survival rate of MSCs transplanted into humans from tissue engineering. Happening.
The article points out that human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are ideal for tissue engineering. However, because of its low survival rate, it limits the therapeutic effect. The researchers found that hMSCs are closer to hypoxia (0.1% O 2 ) in vivo than in hypoxic environments (1%-5% O 2 ) in vitro. In this anoxic environment, hMSCs are unable to accommodate very limited internal glucose stores and essentially zero ATP reserves in the absence of exogenous glucose. In the case of such a low level of exogenous glucose, the lack of a mechanism for down-regulating energy turnover leads to a rapid depletion of the energy reserves of hMSCs, which directly leads to its extremely low survival rate.
Oxygen conditions below 0.1% present the post-transplant environment
The concentration of oxygen in the function of the mammalian tissue is about 2%-10%. For example, the oxygen concentration in the MSC (Mesenchymal Stem Cell) microenvironment (niche) in the bone marrow is 2% to 8%. Oxygen content plays an extremely important role in providing steady-state energy requirements for human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), survival, and ultimately driving function after transplantation. but,
The application of hMSCs in tissue engineering, especially the oxygen concentration requirements in vivo in the early post-transplant period, is unclear.
In this study, hMSCs were first planted on tissue engineering carriers and maintained at an oxygen content of 0.13% ± 0.06% for up to 24 h. The oxygen concentration is lower than the concentration of soft tissue ischemia in the body of mice, and the oxygen concentration of the microenvironment of the human tumor is 0.3% to 4.2%. The explanation for this very low concentration of oxygen consumption is that in the early stage after transplantation, the hMSCs microenvironment has substantially no blood supply of oxygen.
It is very challenging to accurately study the oxygen concentration of cells in vivo. The authors attempted to study the growth of hMSCs in the range of 21% to 0.1% oxygen by establishing an expression of anoxic biomarkers. It was found that 0.1% oxygen content best reflects the true state of hMSCs in vivo. Under these conditions, cells after transplantation showed a high degree of inhibition of mitochondrial activity. In vitro, 0.1% oxygen concentration was the only one that induced hypoxia marker expression and significantly down-regulated mitochondrial activity. The results show that the 0.1% oxygen content best reflects the hMSCs in the living state on the tissue engineering platform, compared with the oxygen content in the state of extensive release, the growth rate is faster and larger.
Anoxic condition control
Anoxic conditional simulations were performed by the pro Ox-C-chamber system (C-Chamber, C-347, Biospherix, New York, NY). The oxygen content in this chamber is maintained at 0.1, 1, 5, or 21%, mixed with 5% CO2, and equilibrated with N2.
For cell culture under hypoxic conditions, hMSCs were cultured in 24-well plates at 12,000 cells per square centimeter.
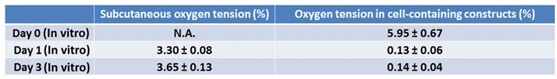
The top panel shows oxygen content measurements at the subcutaneous and hydrogel stent center points after stem cell transplantation.
The data are data from 0 days, 1 day, and 3 days, respectively.
extend
In addition, the hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow, the oxygen content in the surrounding environment also plays an important role in the bone marrow microenvironment. The hypoxic environment results in HSCs at low levels of reactive oxygen species, resulting in better self-renewal capacity and ability to rebuild bone marrow. Considering oxygen content as a component of the stem cell microenvironment is a relatively new concept, but more and more studies have been confirmed in various stem cells.


For details of the required products, please contact the local office of Beijing Beihui Technology Co., Ltd., or send an email to
Female Nourishing Products Plant Extract
Female Nourishing Products Plant Extract,Green Tea Extract,Red Clover Extract,Polygonatum Sibiricum Extract
Fufeng Sinuote Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.sinuotebio.com