
On May 17, 2016, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) released its 2015 annual report, in which Alessandro Spina (A), official of the Data Protection Office of the European Medicines Agency, and Frank Pasquale (F), professor of law at the University of Maryland, discussed big data. Opportunities and challenges in the application of health management and drug supervision. Let's take a look at their insights in this regard.
On May 17, 2016, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) released its 2015 annual report, in which Alessandro Spina (A), Data Protection Office of the European Medicines Agency, and Frank Pasquale (F), Professor of Law, University of Maryland, USA, discussed big data in health. Opportunities and challenges in management and drug supervision.
Q: Big data is the analysis and use of information. What can it bring to health management?
F: We can think about big data, velocity, variety, and volume through 3 Vs.
Velocity Speed: I hope to quickly detect side effects or adverse consequences after the drug is on the market. The sooner you get the patient's record, the sooner you can detect an abnormality that can be discovered based on a certain population.
Variety category: This is related to new sources of data, such as “quantifying self†or self-monitoring, using different biosensors worn on patients or in mobile phones to collect different data. This microscopic monitoring allows the analyst to better understand the effects of a particular dose of medication or a different medication taken by the patient.
Volume Capacity: Collecting a large amount of information about a patient's individual helps to compare the effects of their own treatment. The more the doctor understands the patient's past treatment results, the better the decision can be made.
Q: What challenges and opportunities will be encountered when using big data for drug regulation?
A: First of all, the difference between health data and non-health data is somewhat blurred. Non-healthy data, such as geolocation and lifestyle data, can be used to speculate on a person's important health. Collecting information on the actual use of the drug in a controlled environment (such as in clinical trials) can be used as health data.
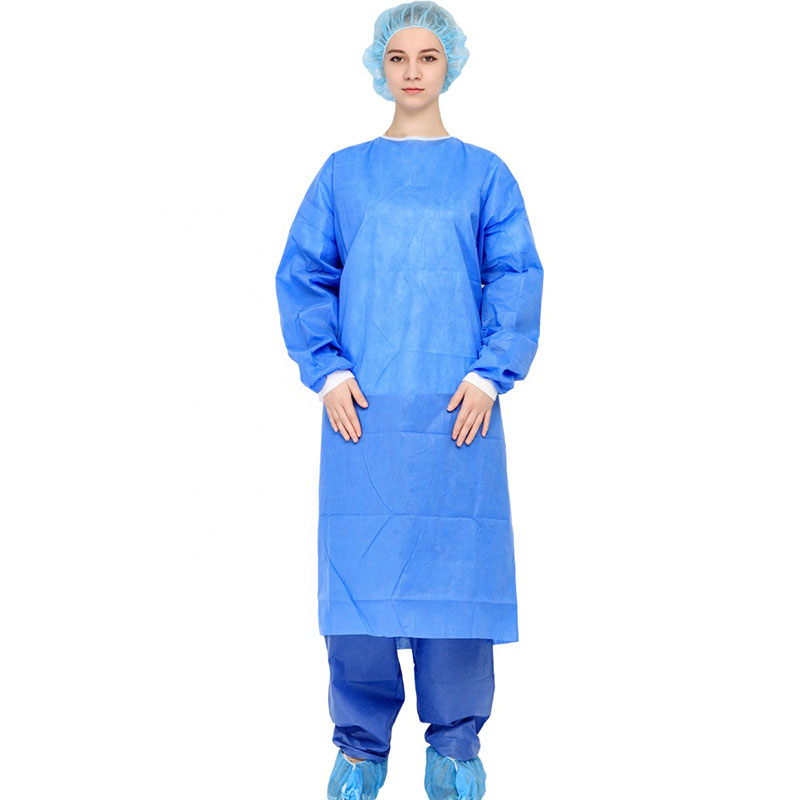
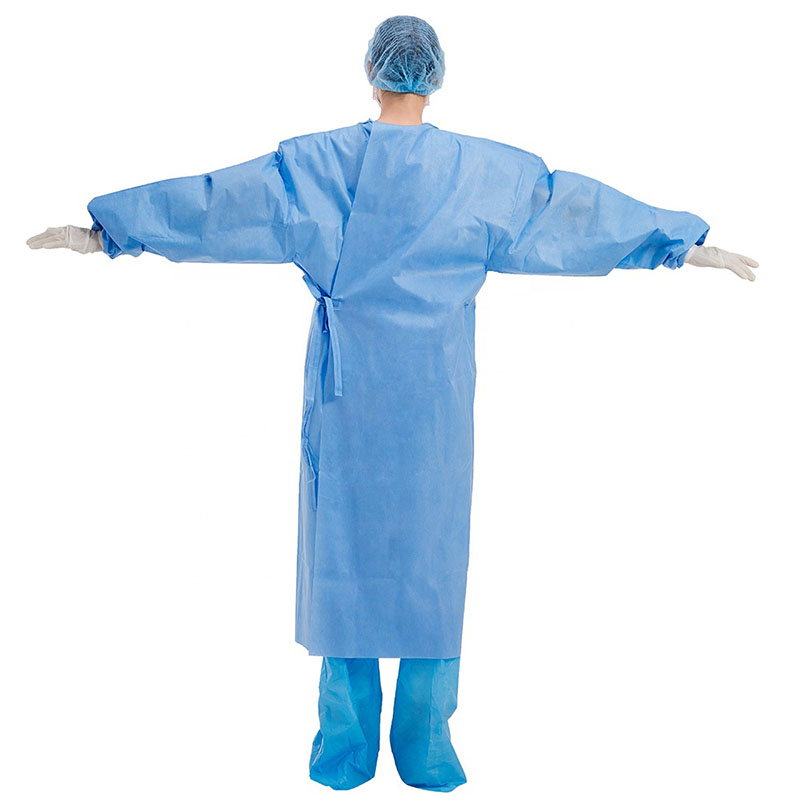
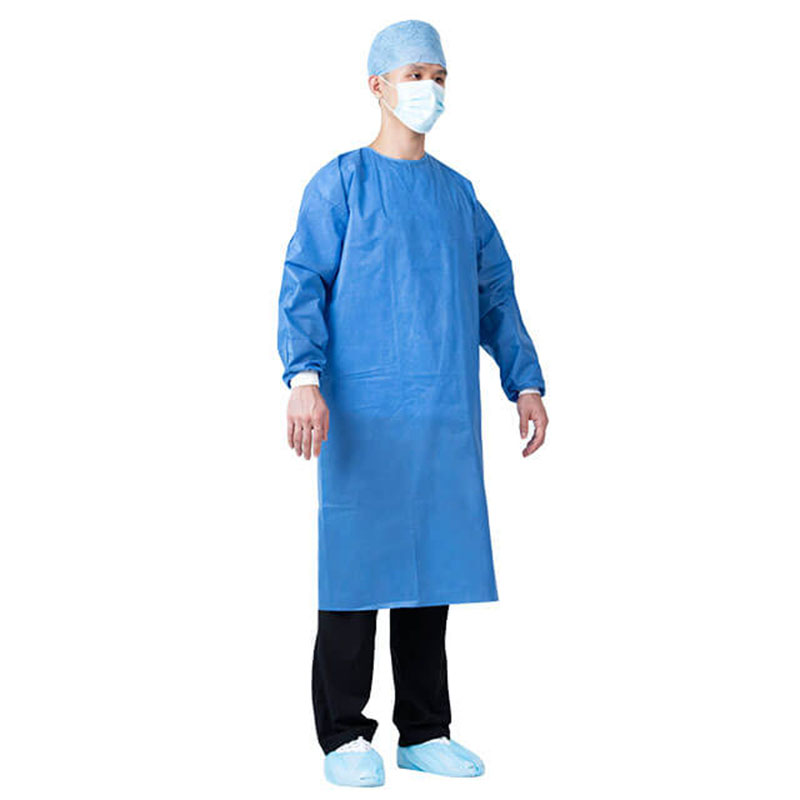
It can be used for surgical operations, patient treatment; epidemic prevention and inspection in public places; disinfection in virus-contaminated areas; and can also be widely used in military, medical, chemical, environmental protection, transportation, epidemic prevention and other field
By setting a protective collar, the neck of the operator can be kept warm and protected. The provision of a hand guard is helpful for the surgical staff to temporarily place their hands in the hand guard while waiting during the operation, which plays a protective role and is more in line with the principles of aseptic operation and occupational protection.
By setting the shrinking cuffs, it is beneficial to make the cuffs fit the wrists, prevent the cuffs from loosening, and prevent the gloves from slipping off during the operation and the operator's hands are exposed to the gloves.
The design of the new humanized protective surgical gown has been improved in the key areas of the gown. The forearm and chest area are double-thickened, and there are handguards in front of the chest and abdomen. By arranging reinforcing sheets (double-layer structure) in key areas, it is beneficial to improve the water-permeability of surgical gowns and improve safety.
surgical gown,disposable surgical gown,personal protection,medical equipment
Shanghai Rocatti Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.shljdmedical.com