Castanea sinensis is born in hills and mountains at an altitude of 100-1800 meters. It is widely distributed in the south of the southern slope of the Qinling Mountains and north of the Wuling Mountains. It is one of the important woody grain plants in China. The flowering period is from May to July, and the fruit is from September to October. The fruit can be made into chestnut powder or canned food, and the wood can be used for sleepers, buildings and the like. However, in the past few years, during the planting process, the Castanea henryi fruit often showed fruit drop phenomenon. Therefore, today Xiaobian talks about the cause and control measures of the abnormal fruit drop of Castanea henryi.

1 Causes of falling chestnut
1.1 Bad flower bud differentiation
Castanea chinensis is a monoecious, cross-pollinated plant. The male inflorescences are arranged in a spiral arrangement of male flowers, and the number of male flowers is very large. It has a special fragrant smell and can induce insects to impart pollen. The male flowers of the growing female flowers are short and thick, and generally there are 1 to 3 female flower clusters with total mites outside. The female flower has 8 stigmas, which have strong developmental branches and the resulting female branches can differentiate the female flower weak branches. The inability to differentiate female flower factors has a great influence on the differentiation of female flowers. Nuts vary in size due to different varieties, and abnormal weather affects the development of nuts, causing fruit drop.
1.2 Variety of mixed, inferior
Due to a large number of artificial cultivation and constant natural selection, the varieties of Castanea henryi are inferior and better, and each variety has great differences in morphological characteristics, yield, fresh weight, tree height, ground diameter, fruiting period, resistance, etc., resulting in high and low yields. Disparity. According to the survey, 80% of the existing varieties are inferior varieties, and most of them have abnormal fruit drop phenomenon (Table 1).
Table 1 Investigation on abnormal fruit drop phenomenon of different Castanea henry varieties
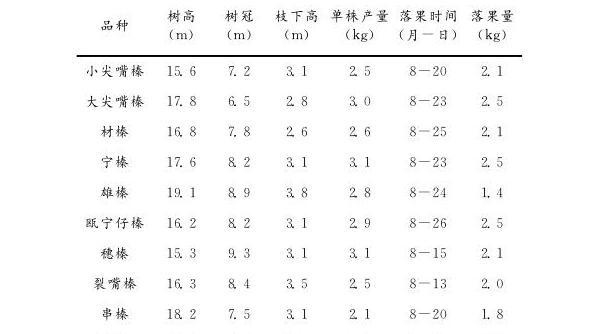
Note: The data in the table is the results of the 2014 survey.
1.3 Management is extensive, poor growth
Because most of the Castanea henryi grows in high altitude areas, the traffic is inconvenient, the daily management is difficult to reach, and most of the traditional management methods: slash and burn, less fertilization, less tending, resulting in poor growth of the tree, less vicious circle, size The annual phenomenon is serious.

1.4 Poor site conditions, poor tree growth
According to the survey, most of the forest land cultivated by Castanea henryi is distributed in high mountainous areas, most of which are of the type III-IV. The soil fertility is poor and the soil layer is thin. Soil improvement is not carried out in time to increase fertility, resulting in slow growth and yield of Castanea henryi. Low, gradually become a small old tree (Table 2). Due to the inferiority of the tree body, the branches are long and have many branches. The crown is rapidly enlarged and the result is moved outward. The tree is weak, the branches, especially the lower branches, die, and the ineffective volume expands. Finally, the tree is dead and the canopy is broken. As a result, the yield is low.
Table 2 Abnormal results of different site types
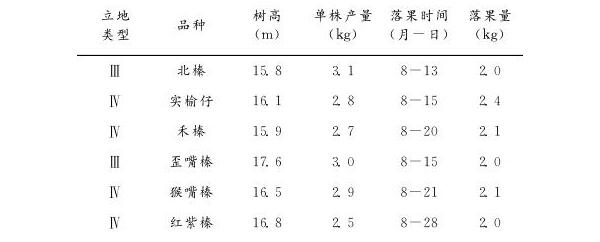
Note: The data in the table is the results of the 2014 survey.
1.5 There are many types of pests and diseases, which are serious
There are dozens of pests and diseases that damage the chestnut, which can damage branches, trunks, flower buds, preserves, fruits, etc., mainly including pests such as chestnut bee, red spider, chestnut blight, powdery mildew and root rot. Since most of the chestnut orchards have not adopted effective pest control measures, pests and diseases have seriously affected the growth and yield of Castanea henryi.
2 Governance technology
2.1 Deep chestnut garden, improved soil
The Castanea henryi plantation is mainly mountain red soil clay, which was changed to soil before harvesting in the same year. Dig deep trenches on both sides of the young trees, 40cm wide and 30cm high, the length is equal to the crown, the sand is filled in the ditch, and 20~50kg of organic fertilizer or straw is applied to each hole. In the second year, the soil was changed in the north and south of the canopy, and it was rotated once every other year until all the soil in the garden was improved.
2.2 Emphasis on the application of base fertilizer
At the end of October, Castanea henryi has been fully matured. In order to ensure the normal growth of the chestnut and the nutrition of the tree in the next year, the organic fertilizer should be applied in time. According to the age, tree potential and yield, the amount of fertilizer applied should be determined. The nutrients provided by the base fertilizer should account for the total amount of fruit trees throughout the year. About 70% of the fertilizer needs to be applied, and 5000 kg of organic fertilizer is generally applied per acre. Radiation fertilization is applied during fertilization. At the same time, the vitex and weeds in the mountainous area can be used. After mowing in the summer, it can be applied under the tree or covered in the tree tray. This can increase the soil organic matter and prevent the evaporation of soil moisture to achieve fattening. The role of water retention.

2.3 Trim and rejuvenate the tree
Timely update and trim the various types of branches to keep the chestnut tree growing and the old weak branches rejuvenated. The Zhongyong branch cultured branch group was selected from the new shoots germinated by the bud bud, and the result was obtained in the second year. For trees with small tree age and dense tree growth, it is necessary to remove dense branches and overlapping branches in time, and the outer branch groups are retracted from the 2 to 3 year old branches, reducing growth points and concentrating nutrients. The chestnut garden with large tree age, extremely weak tree and thin soil has to be renewed and trimmed in a large area, so that the branches are evenly distributed on the main side branches, and the results can be obtained in the same year.
2.4 Prevention of pests and diseases
The main pests and diseases of the reclaimed chestnut garden include chestnut blight, powdery mildew, root rot, anthracnose, chestnut bee, chestnut glutinous rice, chestnut glutinous rice and so on.
Pest control: It can be controlled by using 20% ​​Avi's pine emulsifiable concentrate 1000 times and 80% dichlorvos emulsifiable concentrate 1000 times.
Disease control: can be controlled with 25% prochloraz 1000 times solution, 70% mancozeb 700 times solution, 5% Jinggangmycin 500 times solution, 10% difenoconazole 1500 times solution.
3 governance effect
Table 3 Investigation of abnormal fruit drop in different bases
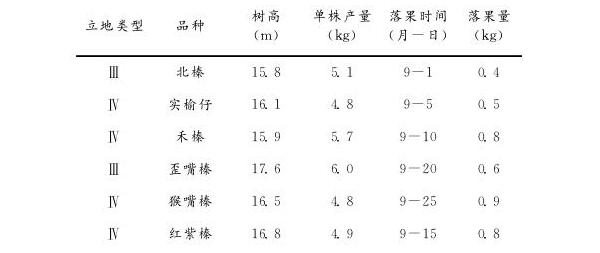
Note: The data in the table is the results of the 2016 survey.
Through the implementation of the above-mentioned measures, significant effects have been achieved in the management of the abnormal fruit drop in the chestnut garden (Table 3), and the yield and quality of Castanea henryi have also been improved to some extent.
For the wonderful pictures and popular comments about the abnormal fruit drop of Castanea henryi, you may be interested in the following recommended contents. Welcome to read.
Pet Training Pads,Pet Absorbent Dog Pee Pads,Disposable Puppy Pet Training Pads,Reusable Washable Pet Training Pads
Honghu Danielle Sanitary Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.daniellecn.com