[Scientific Frontline]] Using Handy PEA and Clark Oxygen Electrodes to Demonstrate the Toxicity Mechanism of Nano-CuO to Microalgae
Welcome to the WeChat public number "Lufthansa Technology Group"! Company official website:  Article link https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2018.1498928
Article link https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2018.1498928
The application of nanomaterials is one of the most important revolutions of the 21st century. Nanomaterials have been widely used in various fields of human life such as coatings, textiles, agricultural fungicides for cosmetics, automobiles and various articles. However, while nanomaterials bring convenience to human life, it poses a potential threat to the ecological environment, the safety of plants, animals and humans.
Nano-copper oxide (CuO NPs), which is a nanomaterial, is widely used in human life. Recently, it has been found that CuO NPs may pollute the environment and cause toxic effects on plants and other organisms.
In the early stage, it was believed that the damage of nanomaterials to organisms was mainly due to its destruction of cell structure and oxidative stress. However, little is known about the effects of nano-CuO on two of the most important metabolic pathways in biology: photosynthesis and respiration. Moreover, the specific sites and mechanisms for the large-scale production of reactive oxygen species ROS caused by nano-CuO toxicity are not clear.
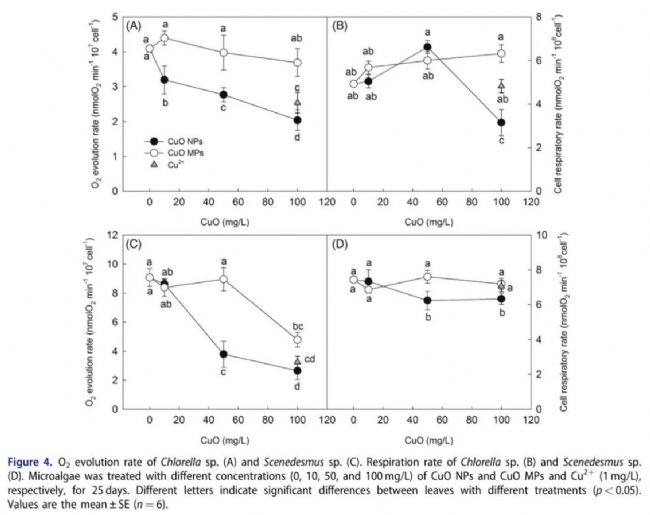 Effects of CuO NPs on photosynthetic oxygen evolution rate and respiratory oxygen consumption rate of Chlorella and Scenedesmus
Effects of CuO NPs on photosynthetic oxygen evolution rate and respiratory oxygen consumption rate of Chlorella and Scenedesmus
Recently, Professor Gao Huiyuan and Professor Wang Wei from the College of Life Sciences of Shandong Agricultural University cooperated to study the rapid chlorophyll fluorescence, photosynthesis and respiration of microalgae by CuO NPs using the Handy PEA multifunctional plant efficiency analyzer and Oxytherm oxygen electrode manufactured by Hansatech , UK. Impact. The toxic mechanism of CuO NPs on microalgae was discussed in depth by electron microscopy, energy spectrum, FFT, PDF, autofluorescence and protein expression determination.
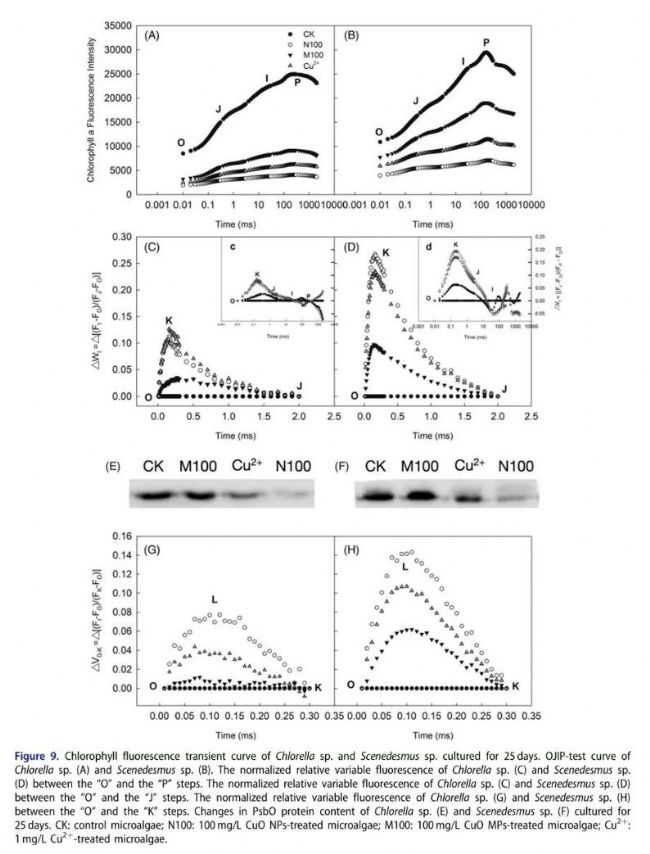 Effects of CuO NPs on Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Oxygen Decomposition Complex Protein of Chlorella and Scenedesmus
Effects of CuO NPs on Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Oxygen Decomposition Complex Protein of Chlorella and Scenedesmus  Changes of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Enzymes in Algae Cells After Treatment with CuO NPs and Specific Occurrence Sites of Reactive Oxygen Species
Changes of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Enzymes in Algae Cells After Treatment with CuO NPs and Specific Occurrence Sites of Reactive Oxygen Species 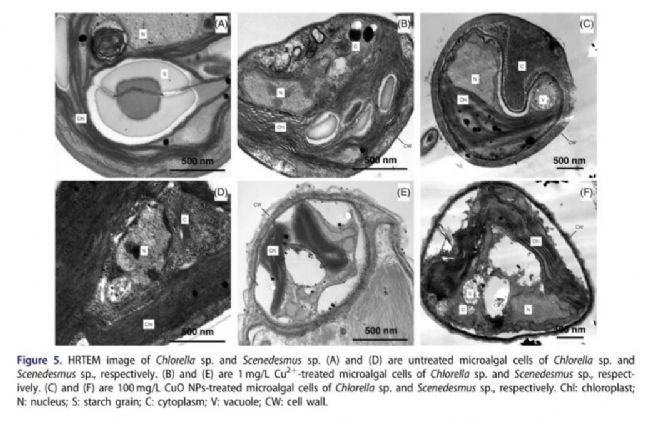 Effects of CuO NPs on the ultrastructure of chlorella and Scenedesmus
Effects of CuO NPs on the ultrastructure of chlorella and Scenedesmus
The study showed that the photosynthetic apparatus of microalgae is more sensitive to the toxicity of CuO NPs than the respiratory mechanism, and the oxygen release complex (OEC) in the photosynthetic electron transport chain is most vulnerable to CuO NPs. Damage to OEC by CuO NPs causes photosynthetic electron transport to be blocked, resulting in insufficient photosynthetic products, resulting in carbon starvation of algae.
In addition, the hindrance of photosynthetic electron transport also increases the excess excitation energy of photosynthesis, leading to the large amount of active oxygen in the chloroplast, leading to oxidative stress of algae cells. Carbon starvation and oxidative stress caused by CuO NPs ultimately inhibited the growth of algae cells.
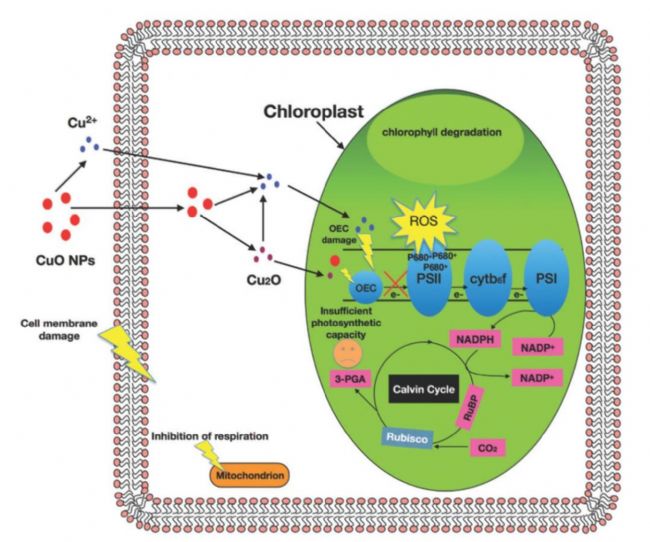 Schematic diagram of the mechanism of CuO NPs toxicity to microalgae
Schematic diagram of the mechanism of CuO NPs toxicity to microalgae
The paper was published in the Nanotoxicology Journal of Toxicology . The first author was Dr. Che Xingkai from the College of Life Sciences of Shandong Agricultural University . This study provides scientific evidence for understanding the damage mechanism of CuO NPs on plants (and organisms), and provides strong support for limiting the emission of nanomaterials to the environment and protecting aquatic and terrestrial ecological environments.
Surgical Aperture Drape,Disposable Aperture Drape,Fenestrated Sterile Drapes,Disposable Fenestration Drape
Xinxiang Huaxi Sanitary Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.huaximedical.com