BACKGROUND: Ischemic cerebrovascular disease is a serious hazard to human health. It is of great research significance and practical value to establish an animal model similar to human cerebral infarction to make it suitable for thrombolytic therapy research. Currently widely used in the method of "blocking the middle cerebral artery to prepare an animal model of regional cerebral infarction", due to the existence of collateral circulation, the degree of ischemia of the affected brain tissue is often inconsistent, and the size and location of the infarct are also different, plus the middle cerebral artery. Blocking requires certain surgical skills, so its application is limited. In addition, the middle cerebral artery occlusion requires certain surgical skills, so its application is limited. Intravenous microthrombotic embolization of cerebral infarction caused by small arteries in the brain is affected by the size of the thrombus, and the embolization site is difficult to control, and its application limitations.
Since 1984, Dietrich and Watson first reported that since the photochemical method was used to induce animal models of cerebral infarction, the method of establishing this model has gradually developed, improved and matured. It has become an important animal model of cerebral infarction and is widely used in the brain. Research on neurobiochemistry, physiology, pathology, and prevention of infarction. Here I describe an experimental report using photochemical methods to induce the establishment of a model of cerebral infarction.
1. Material preparation
1.1 Animal: Adult Rat, 250 g
1.2 Reagents:
Rose Red (Sigma Aldrich, Steinheim, D)
4% paraformaldehyde (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, D)
1.3 Equipment and consumables:
1.3.1 Small animal anesthesia, brain stereotactic positioning (manufacturer: Reward) 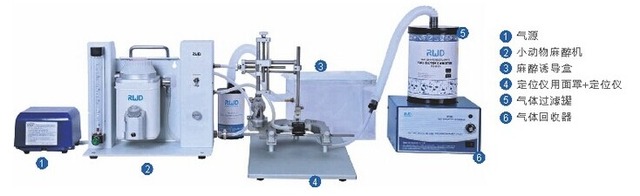
1.3.2 Microsurgery kit (Model: SP0003-R, manufacturer: Reward) 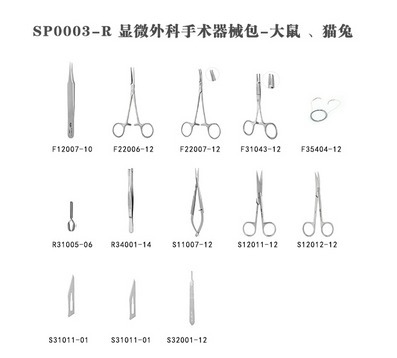
1.3.3 561 mm yellow-green laser (model: R-LG561-100-A5, manufacturer: Reward): used for light stimulation of animal heads. 
1.3.4 Small animal incubator (model: 912-001, manufacturer: LYON/USA) for animal post-operative care. 
1.3.5 SMART3.0 Small Animal Behavior Video Tracking System (manufacturer: Panlab/Spanish) for neurological function through animal behavior after modeling. 
1.3.6 brain mold (manufacturer: Reward), for brain section staining. 
1.3.7 Other auxiliary equipment and consumables (manufacturer: Reward)

2. Experimental methods
STEP1:
Animal anesthesia and head fixation: The animal is induced to enter the anesthesia through an anesthesia machine, moved to the locator device for head fixation and anesthesia maintenance. After a period of stabilization, use the forceps to clamp the foot to test the depth of the anesthesia, when the breathing is gentle, no pressure foot When retracting the reaction, it indicates that the experimental anesthesia is in the middle. In addition, the body temperature maintenance device was turned on to maintain the body temperature of the experimental period (Fig. 1). 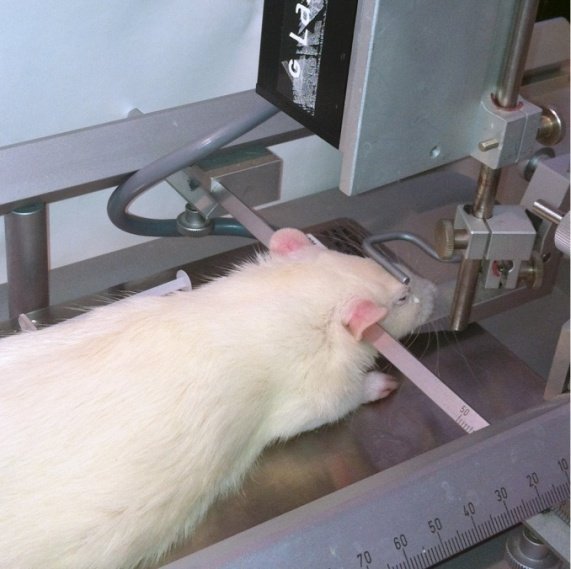
STEP2:
The left femoral vein was exposed and hollowed with a bengal rose polyethylene catheter infusion, and the catheter was fixed with a wire (Figure 2). 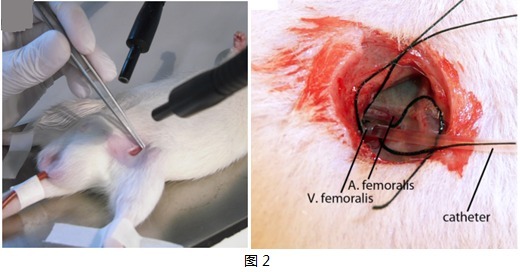
STEP3:
Cut the opening skin (2.0-2.5 cm) longitudinally to expose the skull. In order to avoid wound complications, skull exposure should be performed in a single cut. Gently scrape off a film on the surface of the skull to make the coronal plane and the vector midline and anterior iliac crest clearly visible, exposing the skull surface (Figure 3).
STEP4:
A laser beam with a wavelength of 561 nm and a diameter of 8 mm was stereotactically positioned on the skull AP: 0.5 mm, ML: 3.5 mm surface. The skull was exposed for 20 minutes. Two minutes before the irradiation, rose red (0.133 ml/kg body weight, 10 mg/ml normal saline) was slowly injected into the vein through the reserved catheter. After the injection, the catheter was pulled out and the skin was sutured (Fig. 4). 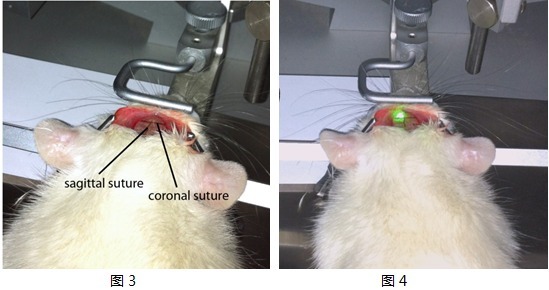
STEP5:
After surgery, the rats were returned to the cage, and the 12 h light and dark cycle in the incubator and the free access to food and water were taken care of.
STEP6:
Control animals received the same experimental procedure, including intravenous venous injections, but no laser illuminates the surface of the skull.
3. Effect evaluation
3.1 nerve function scoring system test 

3.2 Physiological observation 
Alcohol Spray,Spray Hand Sanitizer,Hand Sanitizer Alcohol,Hand Sanitizer Liquid
Wuxi Keni Daily Cosmetics Co.,Ltd , https://www.kenidailycosmetics.com