Li Chunli Li Jieming Red Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd.
1 Introduction
Phthalates plasticizers are a kind of additives that increase the plasticity of polymer resins and enhance the softness of products. They are also the largest variety of additives and consumption to date, among which phthalates are most used. widely. Since phthalates are not polymerized into the plastic matrix, they can be transferred from the plastic to the environment with the passage of time, causing pollution. It can also enter the human body directly through breathing, diet and skin contact, resulting in decreased liver and kidney function, and is mutagenic and carcinogenic. Many countries around the world have passed legislation restricting the use of phthalate plasticizers, including the EU REACH Regulations and the US Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act.
Plasticizers have attracted attention in food safety. First, since May 2011, six kinds of phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, DINP, DNOP, DBP, DMP and DEP have been detected in Taiwanese foods. DIDP. As of June 8, Taiwan has detected 961 foods containing plasticizers. On June 1st, the Ministry of Health issued an emergency announcement to include phthalates (also known as phthalates) in foods that may be illegally added to non-food substances and misused food additives.
Recently, the wave of plasticizer detected in liquor has once again attracted everyone's attention. The addition of plasticizer to liquor may be to make the wine with insufficient vintage look good. Add various tackifiers to cure fake grain wine. The sugar inside produces the effect of sticking a cup to the cup. However, it is also possible that the plasticizer in the liquor product belongs to a specific migration, mainly in contact with plastic products during production or packaging, and the plasticizer is dissolved by alcohol.
At present, China has promulgated the GB/T 21911-2008 "Determination of Phthalates in Foods". Based on this standard, the experiment was optimized by using water bath to remove ethanol and then extracting n-hexane. The new generation triple quadrupole gas chromatography mass spectrometer (TSQ 8000) was used to analyze and detect liquor in 16 A method of phthalate. The effect of background interference in complex matrix samples is substantially reduced by secondary mass spectrometry scanning, and the detection sensitivity of the target compound is improved.
2. Experimental part
2.1 Instruments and Reagents Mass Spectrometer: TSQ 8000 Mass Spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);
Gas Chromatograph: Trace1310 GC with AI l310 Autosampler (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);
Column: TR-Pesticide II 30 m* 0.25 mm* 0.25 μm capillary column (with 5 m precolumn);
Reagents: n-hexane, pesticide residue level;
Liquor: purchased from the supermarket.
2.2 Instrument Method Gas Phase Method:
Column oven: 60oC for 1 min, rise to 220oC at 20oC/min for 1 min, then increase to 280oC at 5oC/min for 3 min;
Inlet: splitless injection, no split time: 1 min, liner: inert without split (item number: 453A1925), inlet temperature is 250oC; carrier gas: constant flow, 1 ml/min;
Transmission line: 280oC
Mass spectrometry method:
The ion source temperature is 250 oC, using the Acquisition-Timed method, SRM scanning, and the specific detection ion pair is shown in Table 1:
3. Analysis of experimental results
3.1 Optimization of fully automatic secondary mass spectrometry conditions (Auto-SRM)
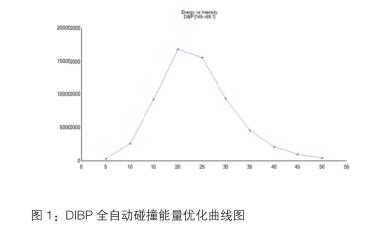
In the gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry process, in order to ensure the accuracy of the qualitative and quantitative, the ion pairs (parent ions and daughter ions) of the analyte, collision energy, scan time, residence time and monitoring reaction must be performed. A series of mass spectrometry parameters such as the number of ions are optimized to achieve the best sensitivity. Using the TSQ 8000 GC/MS, the unique Auto-SRM mode can be used to fully automate the optimization of the secondary mass spectrometry parameters of all compounds and automatically give the collision energy optimization results, which is simple and intuitive, as shown in Figure 1, which saves a lot of money. Analysis time.
In this experiment, under the condition of fixed chromatographic conditions, the optimized instrument parameters, sample chromatogram and standard substance chromatogram comparison, the relative deviation of retention time does not exceed ± 2.5% of the reference material; using multi-ion pair qualitative, relative ion abundance maximum allowable deviation Not more than ±20%, ensuring qualitative accuracy.
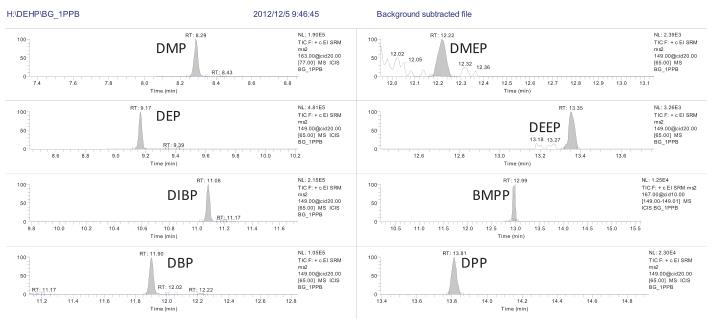
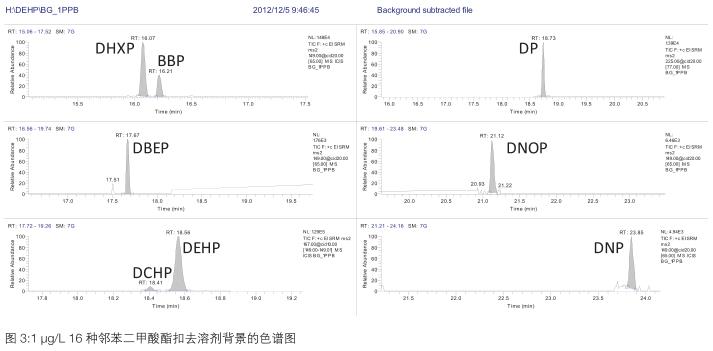
3.2 Chromatographic Separation Results Since the solvent may contain phthalate esters, we have done a solvent control before each sample to eliminate the interference effects in the solvent and eliminate false positive results. Since the ion information of the 16 phthalates is somewhat similar, we have chosen a weakly polar column with good resolution to ensure that the 16 phthalates are separated on the chromatogram. Make qualitative quantification more accurate. The chromatographic separation of 16 phthalates is shown in Figure 2:
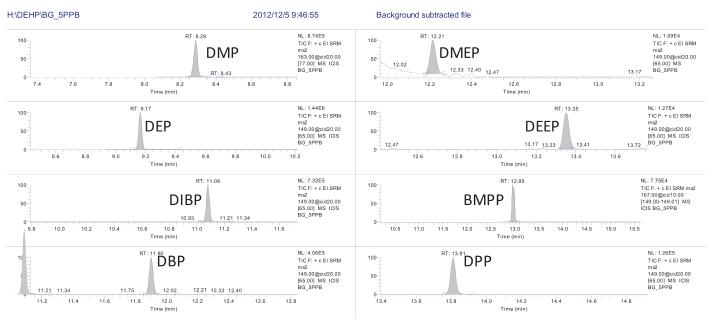

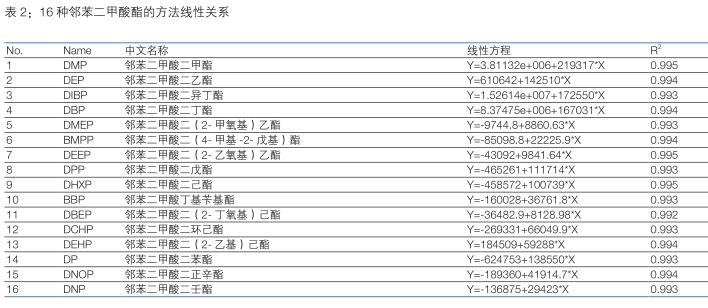
3.3 Standard curve and minimum limit of quantification <br> Preparation of 1 μg/L, 5 μg/L, 10 μg/L, 50 μg/L, 100 μg/L, 500 μg/L with n-hexane as solvent The solution was established to establish a standard curve. The standard curve of each compound is shown in Table 2. The correlation coefficient R 2 is greater than 0.991, indicating that the standard curves of the 16 compounds are linear. Some of the phthalates in the solvent background are interfering. Therefore, it is necessary to subtract the background from the standard solution and then calculate the standard curve to make the standard curve more accurate. The minimum limit of quantification for the 16 phthalate compounds in this experiment was 1 μg/L, see Figure 3. The DEP, DIBP, DBP and DEHP contents in the solvent are estimated to be 20-30% of the 1 μg/L standard, so the minimum limit of quantification is set to 1 μg/L.
3.4 Determination of method precision and recovery rate <br> Weighed liquor samples, added two standard samples of horizontal concentration, and selected the low concentration levels for parallel determination six times. The results showed that the average recovery was 81.5-115%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n=6) was 1.74-4.95%. The recovery and precision data results are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Precision and recovery of the method 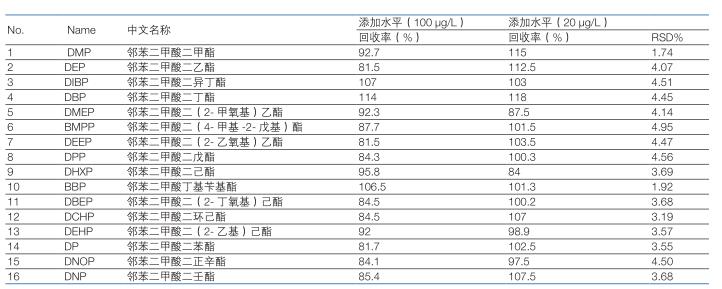
3.5 Actual sample detection <br>According to the pretreatment method described above, the analysis of phthalate residue analysis was carried out on 4 different white spirits commercially available. The test results are shown in Table 4. Where the linear range is exceeded, the quantification is performed after the second dilution.
Table 4: Statistics of actual sample test results 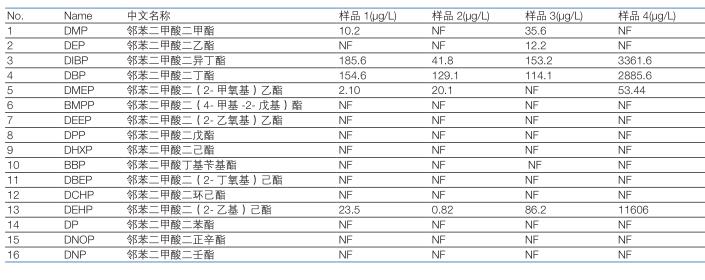
For the detected compounds, the compounds can be further confirmed by the ratio of the mass spectrometric ions of the secondary mass spectrometry to the quantitation ions. The figure below shows that the ion ratio of the DIBP detected in the sample 1 conforms to the standard value, so that it is confirmed that the sample 1 is indeed detected. It is DIBP.
According to the provisions of GB9685-2008 "Sanitary Standards for the Use of Additives in Food Containers and Packaging Materials", phthalate esters are plasticizers that can be used in food packaging materials. They are not food materials or food additives. Artificially added to food additives. The maximum residues of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) and di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) in foods and food additives were 1.5 mg/kg and 0.3 mg/kg, respectively. The results of our sample test showed that DIBP, DBP and DEHP were common in liquor. The content of DBP and DEHP in one sample exceeded the regulation. The DBP content in sample 4 was 2.885 mg/L, that is, the sample content was 1.154 mg/kg. Exceeding the standard of 285%; the content of DEHP is as high as 11.606 mg / L, that is, the sample content is 4.64 mg / kg, exceeding the standard of 209%.
4. Conclusions <br>This method uses ThermoFisher's new generation triple quadrupole mass spectrometer TSQ 8000 to determine 16 phthalate residues in liquor. This method has convenient operation, good selectivity, wide linear range and high sensitivity. Features such as high sensitivity reduce sample size, greatly reduce sample contamination of mass spectrometers, and save on analysis and maintenance costs. At the same time, the ion pair scanning provided by TSQ 8000 can effectively eliminate the false positive interference and make the detection result more accurate. The recoveries were 81.5-115% at the two addition levels of 100 and 20 μg/L, and the relative standard deviations (RSD, n=6) at the concentration of 20 μg/L were 1.74-4.95%. The minimum limit of quantification of this method is 1 μg / L, which can fully meet the detection needs of phthalates in liquor.
enous catheter set,central venous catheter price,central venous catheter kit,central venous catheter triple lumen
Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.honestymed.com